Barrett’s esophagus: Understanding surveillance guidelines
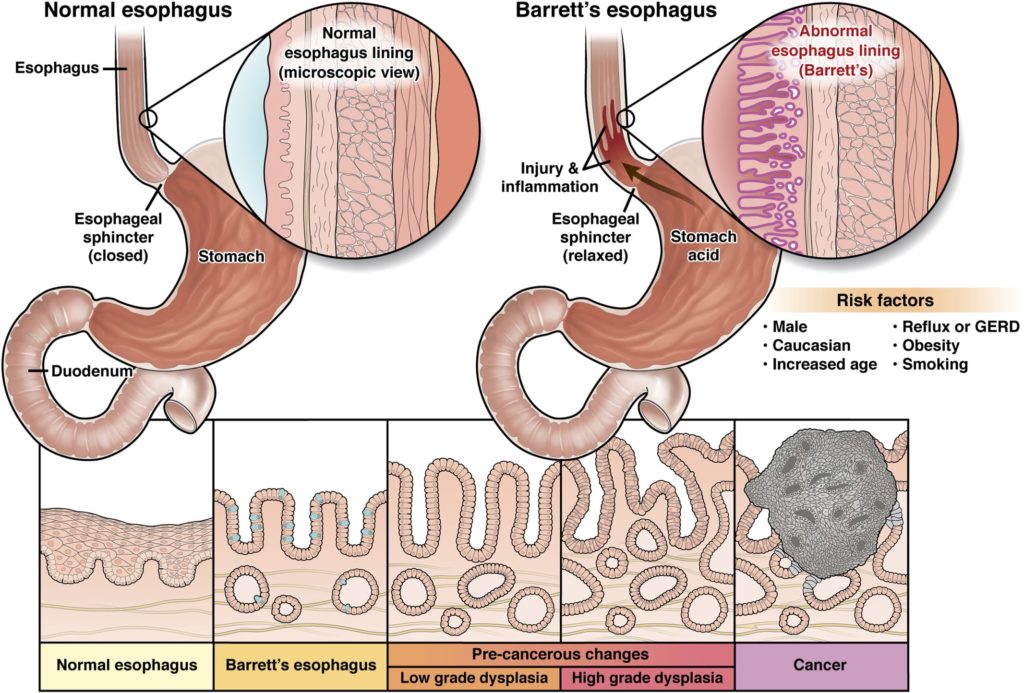
Barrett’s esophagus is when the cells lining the esophagus — the tube connecting the mouth to the stomach — change into the cells lining the intestine. The test for Barrett’s is an endoscopy.
Metabolic-dysfunction associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD): Plant-forward diet

A plant-forward food plan lets you be flexible with food choices, while being focused on adding and enjoying more plant foods.
Obesity: Learn the facts beyond the scale for Hispanic Americans
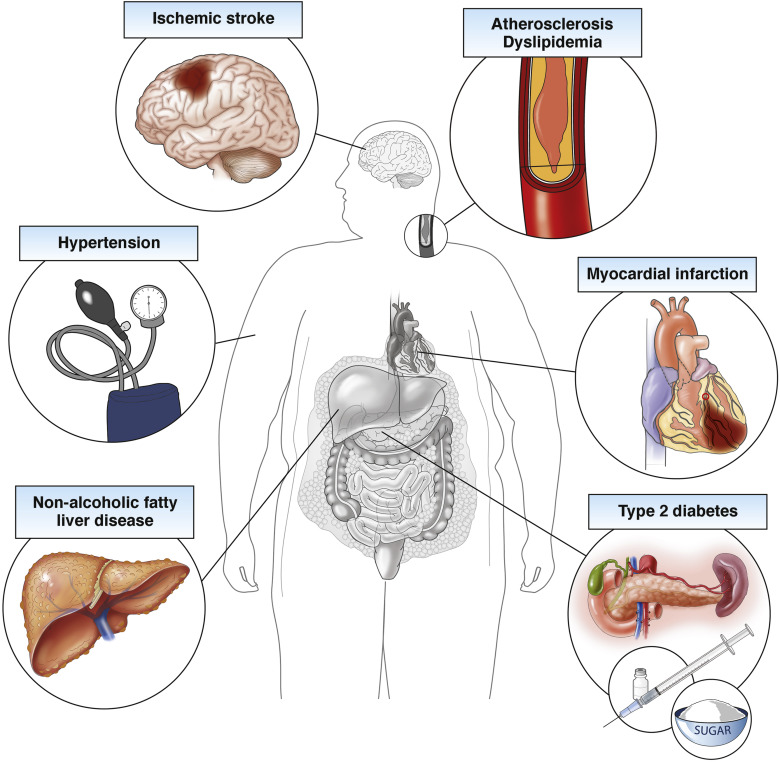
Obesity is a disease that impacts some ethnic and racial groups more than others, including nearly half of Hispanic American adults.
Obesity: Advocacy toolkit

Iron deficiency anemia
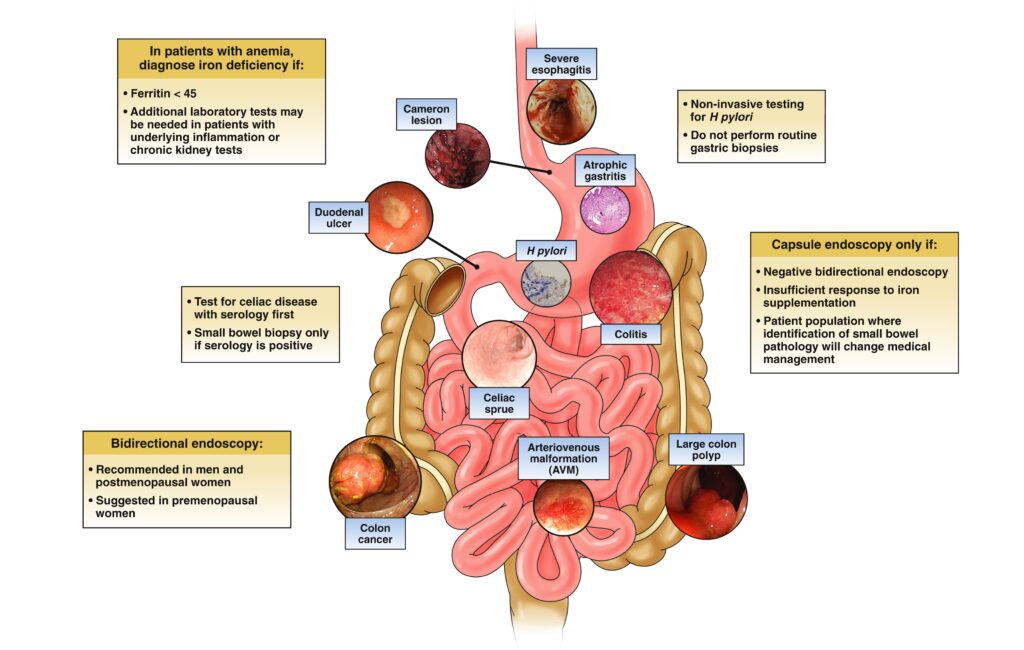
Iron deficiency anemia is the most common type of anemia that happens when you don’t have enough iron to make healthy red blood cells.
Obesity

Obesity is a chronic, complex, and treatable disease. It is associated with having an excess amount of body fat. Obesity is not a choice. Genetic, environmental, and social factors play a role in obesity.
Obesity: MASLD and lifestyle changes – health-promoting habits for weight management

Obesity is a chronic, complex, and treatable disease. It is associated with having an excess amount of body fat. Obesity is not a choice. Genetic, environmental, and social factors play a role in obesity.
Obesity: GERD and lifestyle changes – Healthy habits for weight management

Obesity is a chronic disease in which someone has an excess of fat that negatively impacts their health. The calculation of body mass index (BMI) is typically used to measure if someone has obesity (overweight).
HAES®-centered nutrition therapy for GI conditions
Health At Every Size, or HAES, is a weight-neutral approach to health, independent of weight that can help you achieve health and well-being.
Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) and metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis (MASH)
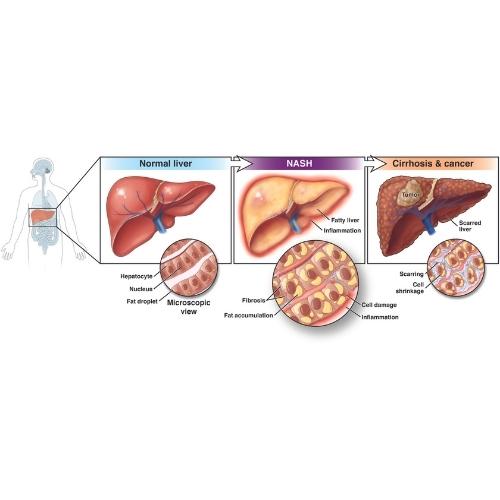
Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) happens when your liver stores too much fat and it is not related to heavy alcohol use. Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis, or MASH, is a more severe form of fatty liver disease that causes inflammation, called hepatitis, and liver cell damage.
