Eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE): From teen to adult care

Eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) is when white blood cells build up in the esophagus and can result in trouble swallowing, heartburn and reflux. As a teen or adolescent with EoE, it’s time to learn how to become comfortable making your own health care decisions.
Celiac disease: Who should be tested
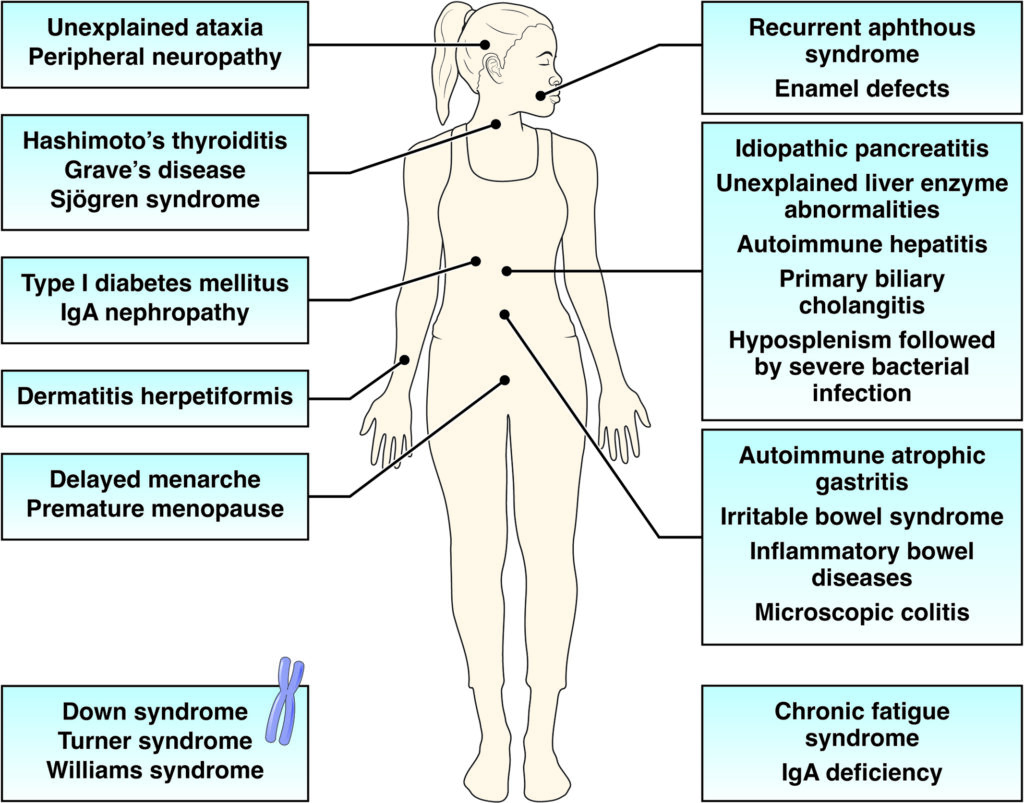
If you’ve been diagnosed with a condition related to celiac disease or have other risk factors, does that mean you should be tested for celiac disease?
Obesity: Learn the facts beyond the scale for Hispanic Americans
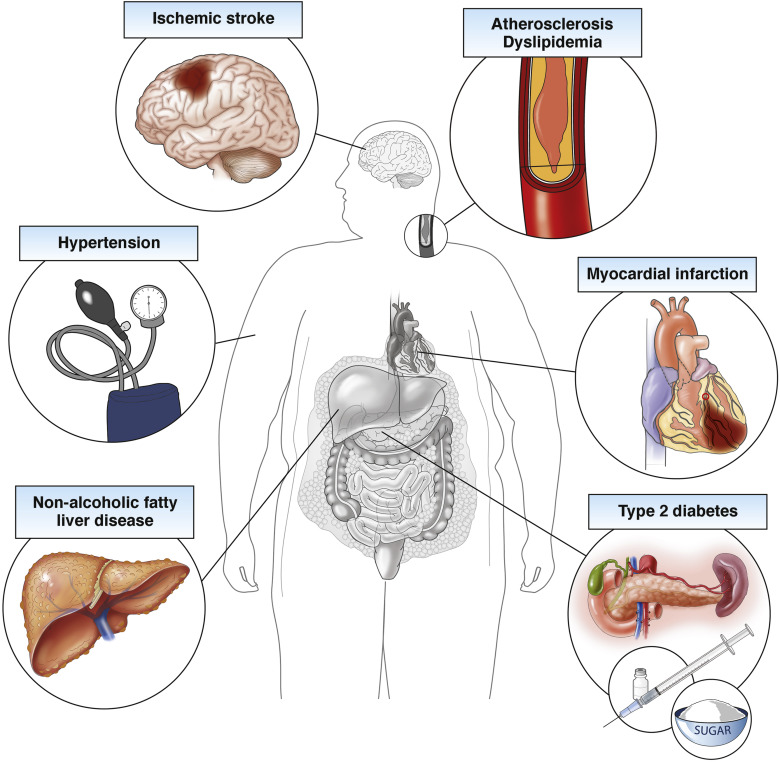
Obesity is a disease that impacts some ethnic and racial groups more than others, including nearly half of Hispanic American adults.
Obesity: Advocacy toolkit

Iron deficiency anemia
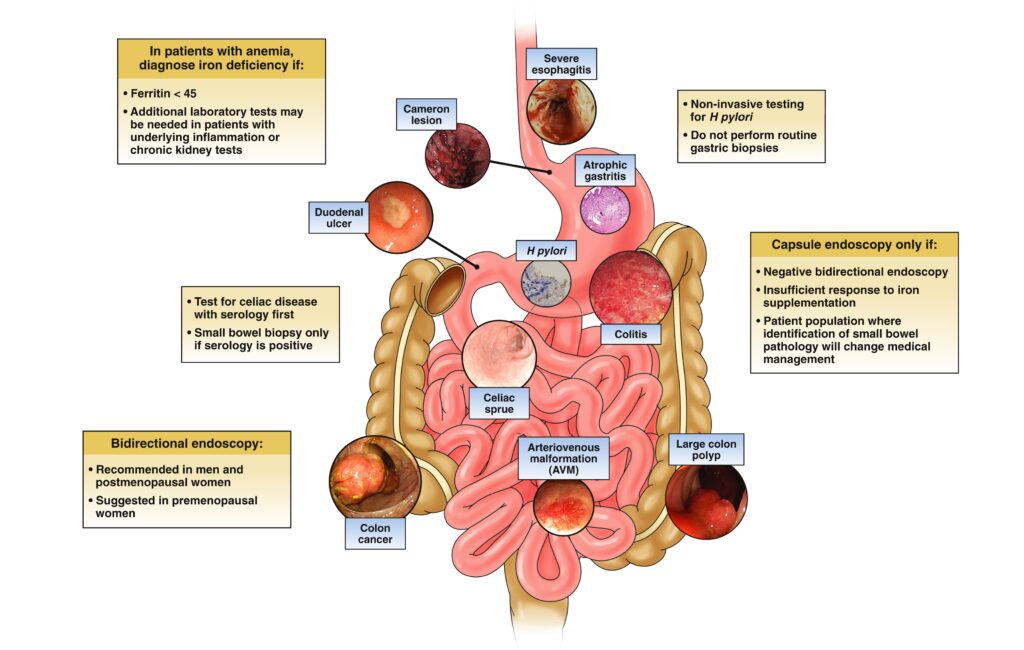
Iron deficiency anemia is the most common type of anemia that happens when you don’t have enough iron to make healthy red blood cells.
Alpha-gal syndrome with GI symptoms
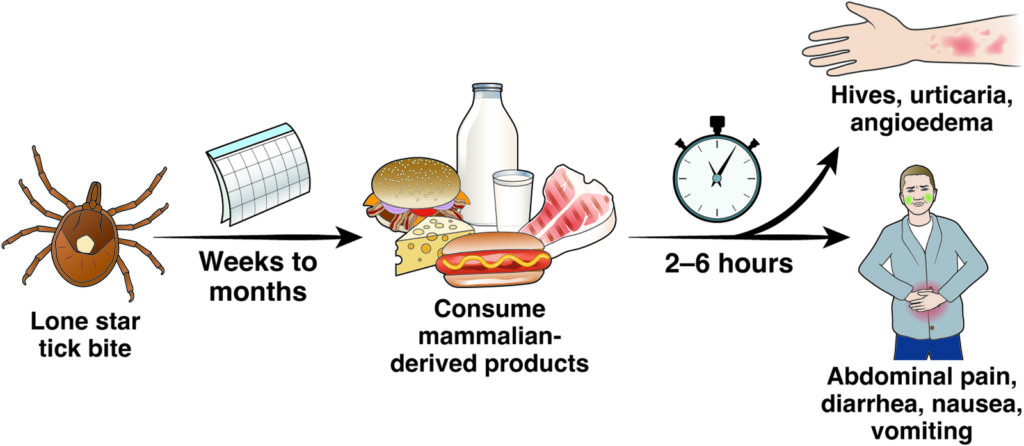
Alpha-gal syndrome is an allergy that causes your body to respond badly after eating meat from mammals and can cause GI or skin symptoms.
Short bowel syndrome (SBS): From teen to adult care

Short bowel syndrome (SBS) is a rare disorder that happens when you don’t have enough small intestine, or it doesn’t work well. As a teen or adolescent with SBS, it’s time to learn how to become comfortable making your own health care decisions.
Trust Your Gut
Obesity

Obesity is a chronic disease in which someone has an excess of fat that negatively impacts their health. The calculation of body mass index (BMI) is typically used to measure if someone has obesity (overweight).
Obesity: MASLD and lifestyle changes – Healthy habits for weight management

Obesity is a chronic disease in which someone has an excess of fat that negatively impacts their health. The calculation of body mass index (BMI) is typically used to measure if someone has obesity (overweight).

