IBD Resource Center
What is inflammatory bowel disease (IBD)?
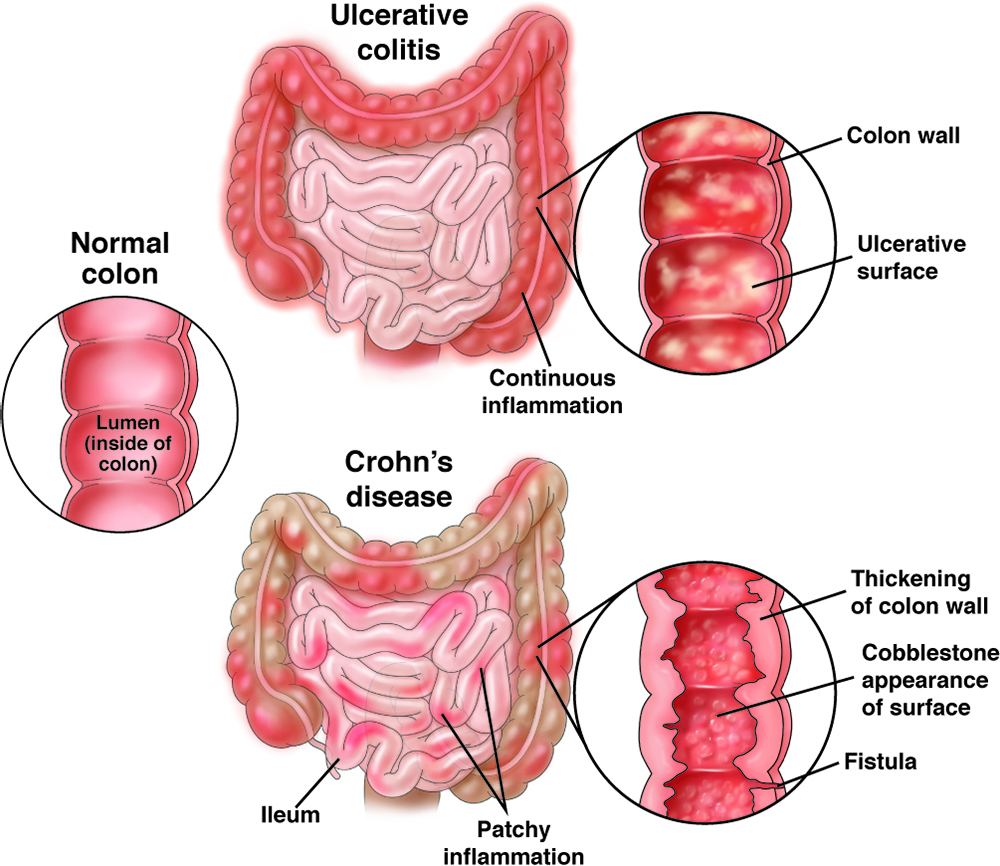
Inflammatory bowel disease, or IBD, is when there is inflammation, or swelling, in the gastrointestinal (GI) tract and a lifelong immune response. The disease causes the body and immune system to think that food, bacteria and other needed things in the intestine are not supposed to be there. With this, the body attacks the cells of the bowels, causing inflammation that does not easily go away. Nearly 3 million Americans are affected by IBD, and the number of people affected continues to grow worldwide.
There are two main types of IBD: ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease. Both are illnesses with times of remission (when you feel well) and relapse (when you feel ill). Symptoms can differ from person to person and depend on the type of IBD.
Related topics
Diet and nutrition in IBD
Good nutrition is important when you have IBD. Staying hydrated, eating enough calories, and choosing foods that are gentle on your stomach can help your body heal and may lessen symptoms during flares. Paying attention to what you eat can help you feel better day‑to‑day.
Vaccine recommendations
When you have IBD, it is even more important to protect your body from infections because they may cause your IBD to flare up. With IBD, your immune system is distracted fighting your own body, so you may become sicker than someone who does not have IBD with a routine infection.
Learn more about general vaccine guidelines and how to talk to your primary care physician and gastroenterologist (GI) about what vaccines you need for your IBD treatment regimen, age and sex.