Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) and metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis (MASH)
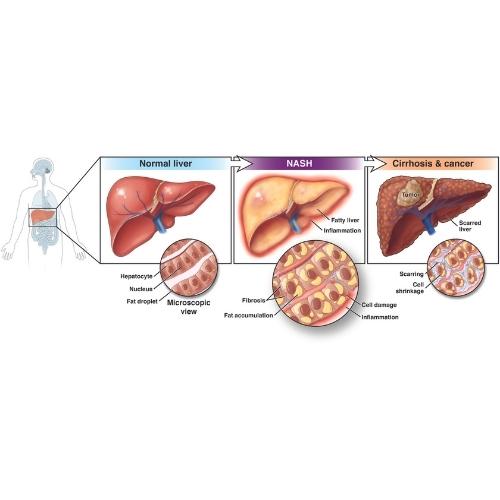
Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) happens when your liver stores too much fat and it is not related to heavy alcohol use. Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis, or MASH, is a more severe form of fatty liver disease that causes inflammation, called hepatitis, and liver cell damage.
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD)
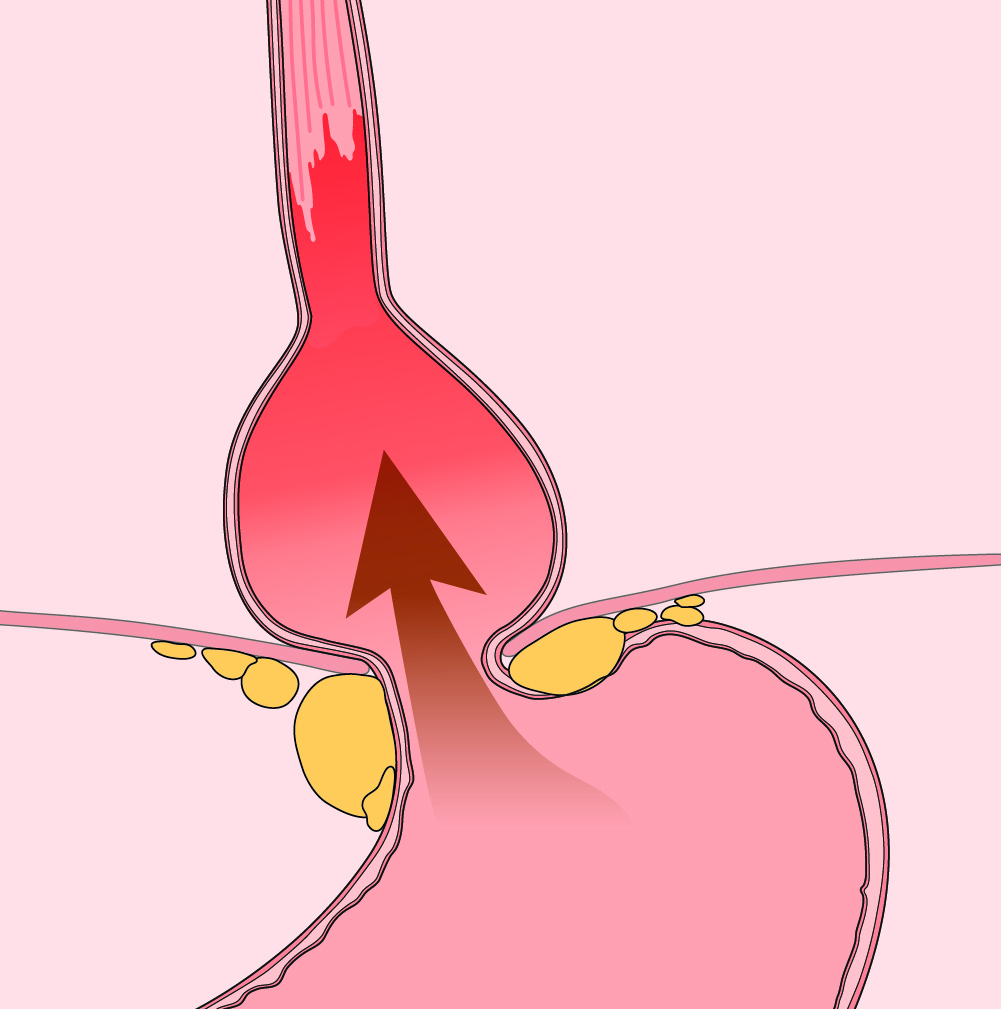
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), or just acid reflux, is when stomach acid frequently flows back into the esophagus. Heartburn is the most common symptom of GERD.
Exocrine pancreatic insufficiency (EPI)
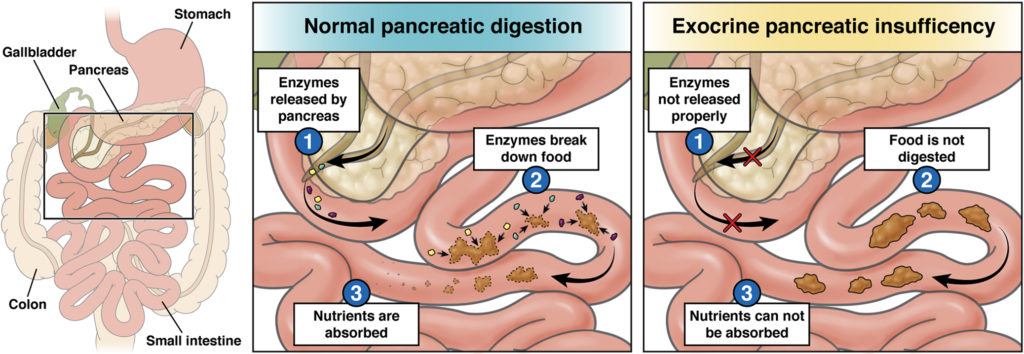
Exocrine pancreatic insufficiency (EPI) is caused by a problem with the pancreas, an organ that plays an important role in digestion. EPI can be difficult to recognize, but once it’s identified, it
can be treated.
Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS)
Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) is one of the common disorders of the large intestine. IBS symptoms can include stomach pain, diarrhea, stomach bloating, constipation and cramping.
Hemorrhoids
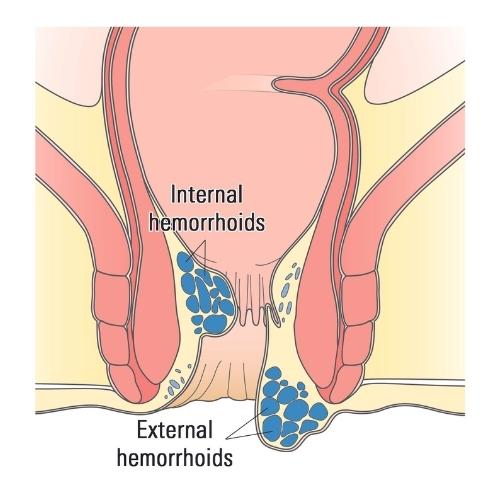
Hemorrhoids are swollen veins around the anus. Swelling can be caused by straining to move your bowels, sitting too long on the toilet, or other causes, like pregnancy, obesity, or liver disease.
Gas
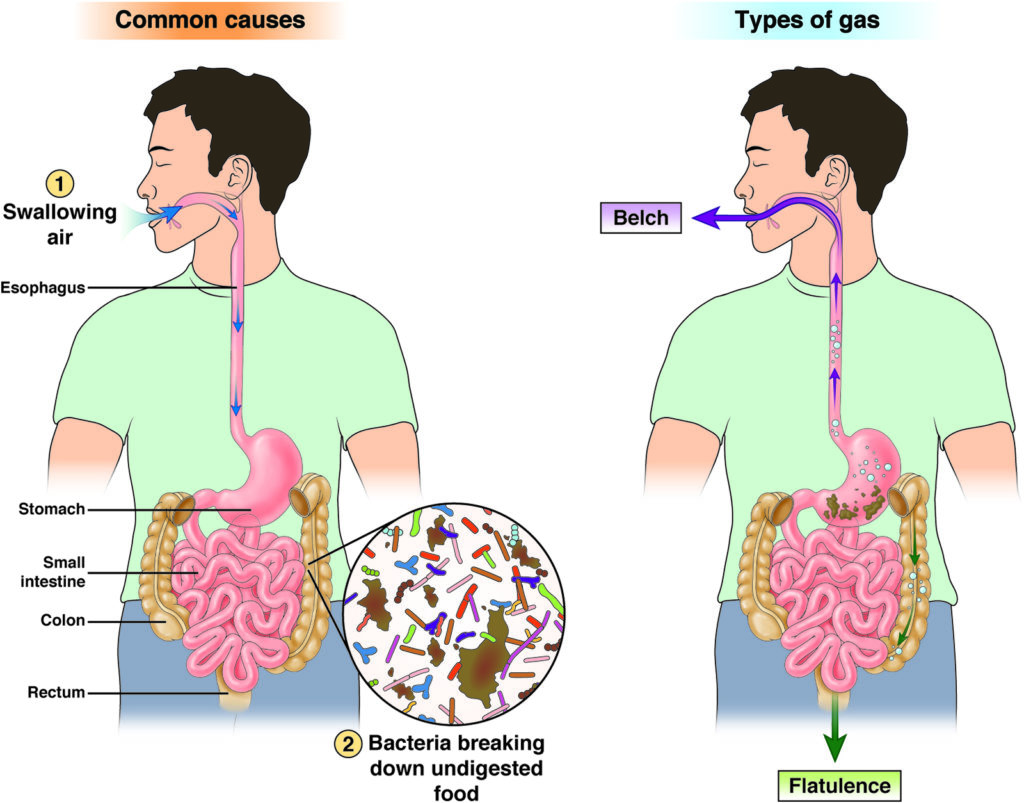
Gas is when air builds up in your small intestine and large intestine. Flatulence is when gas passes through the rectum and belching, or burping, is when gas passes through the mouth.
Eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE)
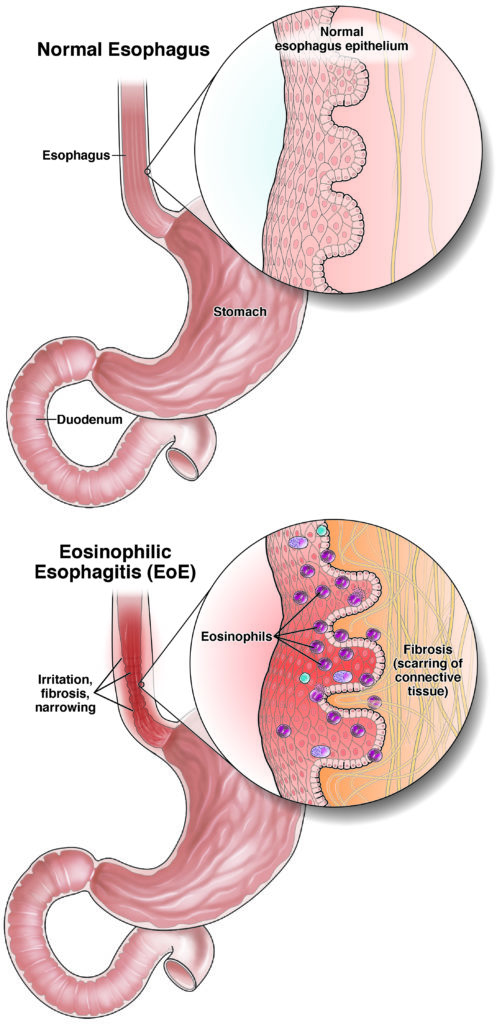
Eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) is when white blood cells build up in the esophagus and may result in trouble swallowing, heartburn and reflux.
Gallstones
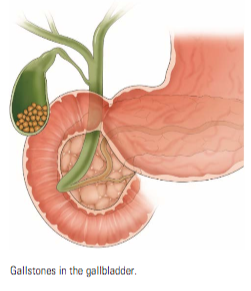
Gallstones are parts of the bile stored in the gallbladder, such as cholesterol and bilirubin, hardened into solid matter. Symptoms can be pain in the upper abdomen, vomiting and sweating.
Gastroparesis
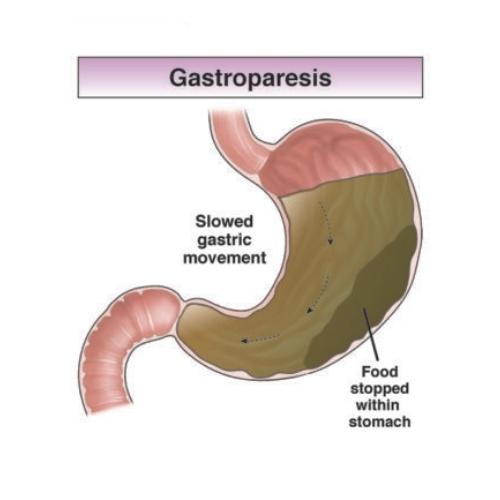
Gastroparesis or delayed gastric emptying is when the stomach has trouble clearing out its contents, possibly due to issues with the stomach muscles, nerves, or brain and spinal cord nerves.
Dyspepsia
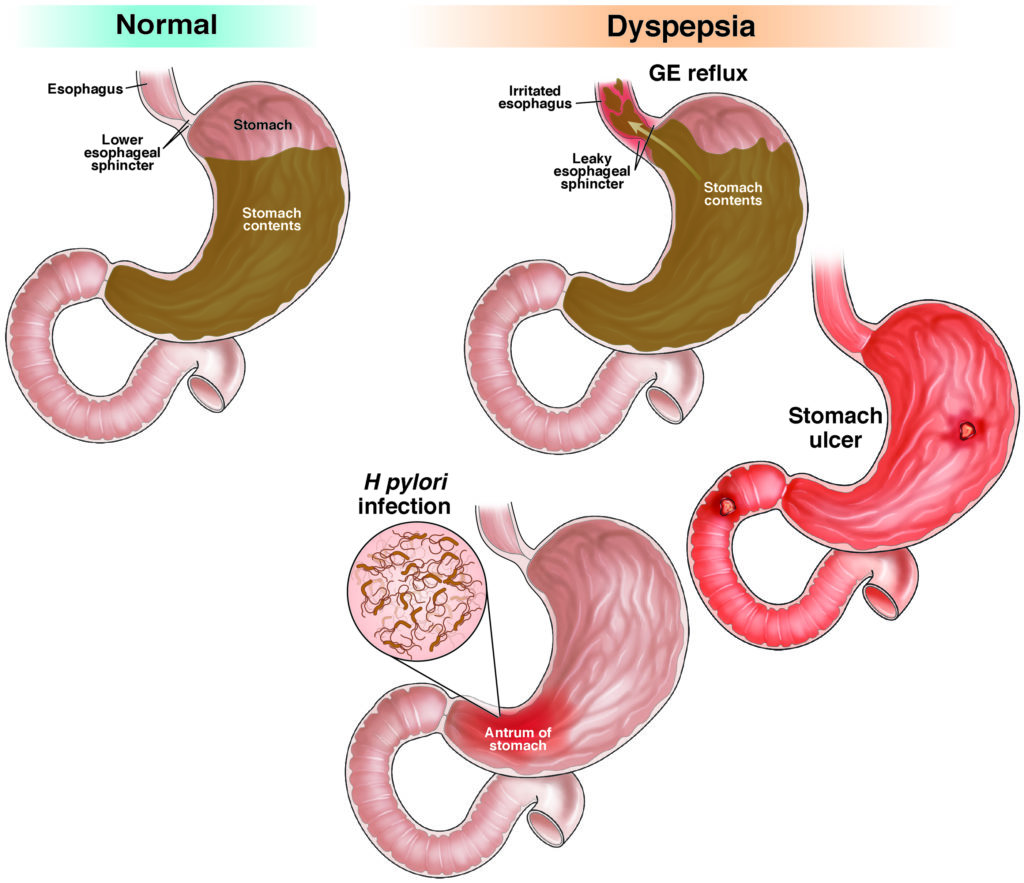
Dyspepsia, or indigestion, may cause upper abdominal pain, burning or heat, and the stomach feeling full during or after eating.
