Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD): Role of fiber
Consuming a wide variety of foods with fiber is important for gut health in patients with inflammatory bowel disease, or IBD.
Gluten-free diet: nutritional value
A nutritious gluten-free diet can help correct and prevent nutrient deficiencies that may occur in celiac disease and non-celiac gluten sensitivity.
Gluten: reading a label
For people with celiac disease, knowing how to read ingredient labels is essential to avoid gluten in foods, beverages and medicines.
HAES®-centered nutrition therapy for GI conditions
Health At Every Size, or HAES, is a weight-neutral approach to health, independent of weight that can help you achieve health and well-being.
Achalasia: nutrition therapy
Symptoms associated with achalasia may include difficulty swallowing, regurgitation, heartburn, weight loss, chest pain and coughing. An altered diet can help.
Gastroparesis: nutrition therapy
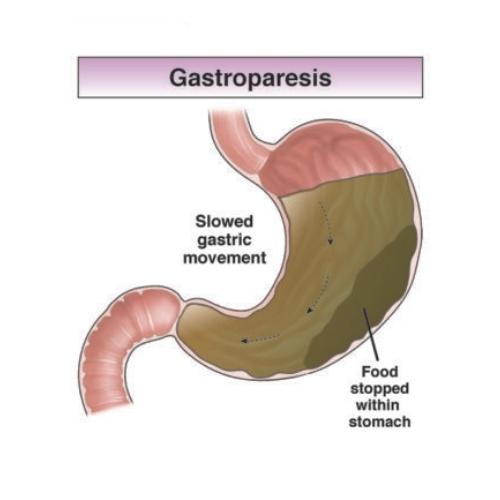
If you have gastroparesis, it is important to find the foods that work best for helping you to feel healthy.
Gluten-free diet
A gluten-free diet involves avoiding wheat, barley, rye, and all foods made with these ingredients.
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD): Diet tips
Diet tips to help reduce symptoms during Crohn’s disease or ulcerative colitis flares or active disease.
Six-food elimination diet (SFED)
The six-food elimination diet (SFED) is often a successful treatment for patients with eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE).
Gentle GI nutrition
Also called the non-diet approach, this approach focuses on finding alternatives besides restrictive diets to help with GI symptoms.

