Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD): Role of fiber
Consuming a wide variety of foods with fiber is important for gut health in patients with inflammatory bowel disease, or IBD.
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD): Diet tips
Diet tips to help reduce symptoms during Crohn’s disease or ulcerative colitis flares or active disease.
Low-FODMAP diet
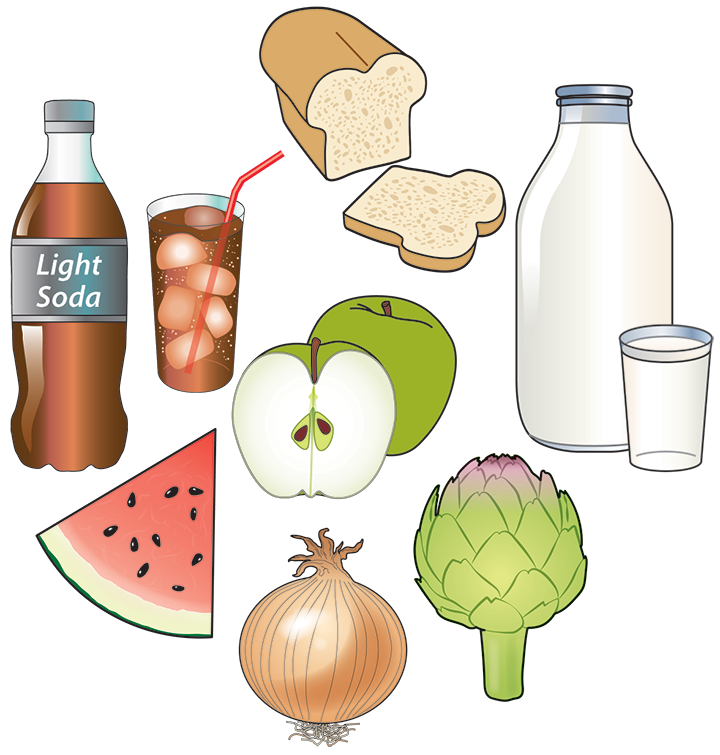
A low-FODMAP diet is low in a group of five sugars found in certain foods, which cause some people to experience bloating, stomach swelling, stomach pain, nausea, diarrhea, and constipation.
Fructose intolerance
Fructose intolerance happens when your body cannot absorb fructose from what you eat or drink.
Pancreatitis
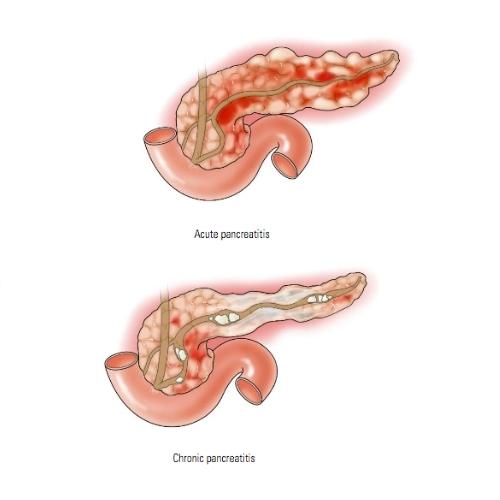
Pancreatitis refers to inflammation (swelling) of the pancreas. It is often caused by gallstones or heavy alcohol abuse. Both acute and chronic pancreatitis symptoms are similar.
Exocrine pancreatic insufficiency (EPI)
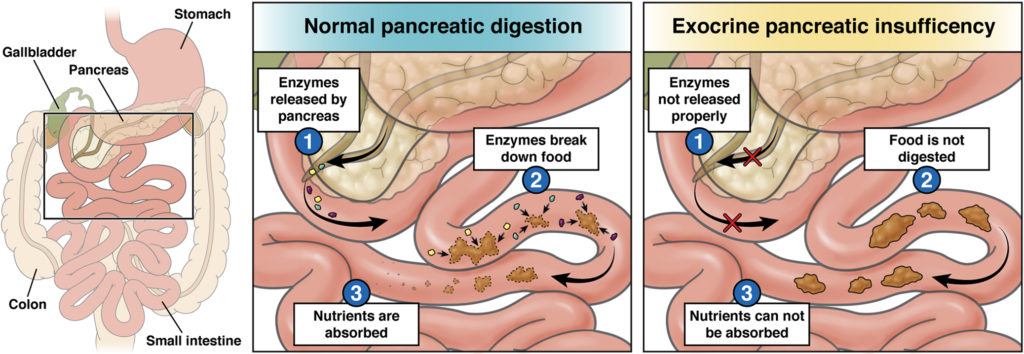
Exocrine pancreatic insufficiency (EPI) is caused by a problem with the pancreas, an organ that plays an important role in digestion. EPI can be difficult to recognize, but once it’s identified, it
can be treated.
Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS)
Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) is one of the common disorders of the large intestine. IBS symptoms can include stomach pain, diarrhea, stomach bloating, constipation and cramping.
Clostridioides difficile (C. diff)
Clostridioides difficile, or C. diff, is a bacterium that can cause gastrointestinal symptoms, like nausea, watery diarrhea, stomach pain and stomach cramps that may be severe.
Diverticulitis
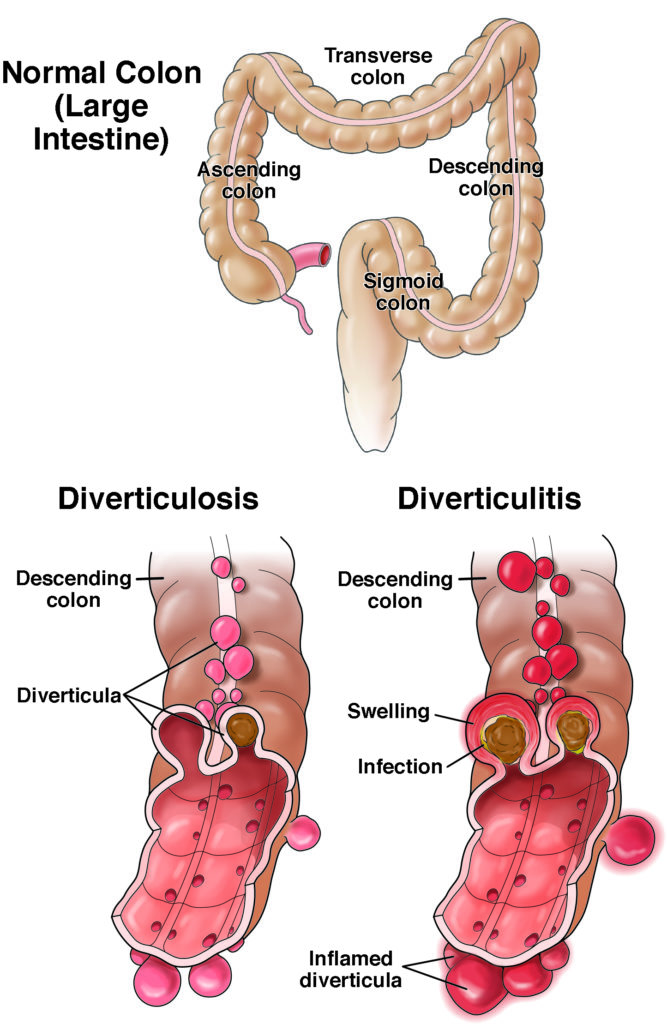
Diverticulitis is when pockets form in the colon wall and become infected or swollen causing pain, cramping, diarrhea, constipation or fever.
Diarrhea
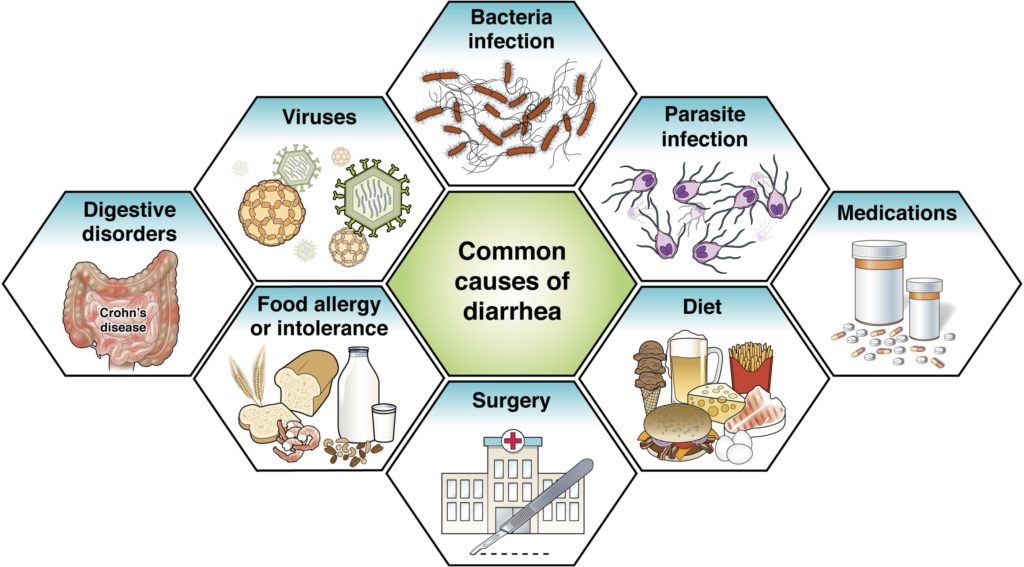
Diarrhea happens when you have watery, loose stools three or more times a day.


