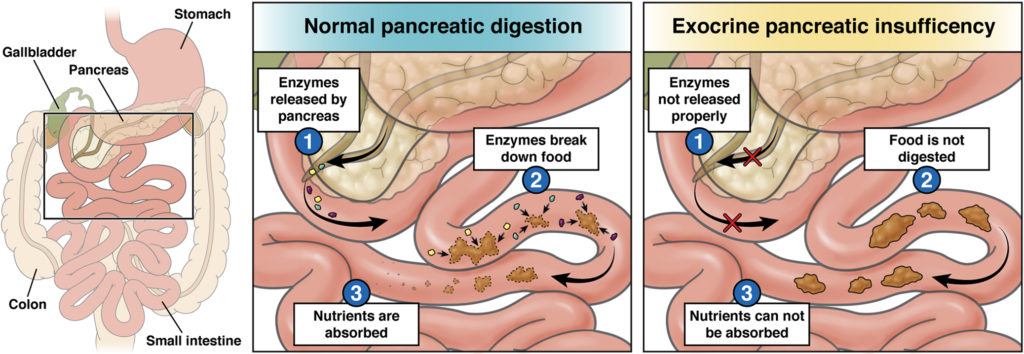
What is exocrine pancreatic insufficiency?
Causes
EPI often results from damage to the pancreas from diseases such as chronic pancreatitis, pancreatic cancer or cystic fibrosis. Removal of some or all of the pancreas or surgery to other parts of the digestive tract (such as the intestines or stomach) may also cause it.
Signs and symptoms of exocrine pancreatic insufficiency
EPI symptoms can range from mild to severe.
The most common symptoms include:
- Gas and bloating.
- Abdominal pain.
- Greasy, oily bowel movements (stools).
- Diarrhea (very loose stools).
- Foul-smelling stools.
- Unexplained weight loss.
Tests for exocrine pancreatic insufficiency
This test is done to look for an enzyme called elastase that is released from the pancreas during digestion. Normally, this enzyme will be found in stool. If little or none is found, it can be a sign of EPI.
For this test, you will be asked to collect one sample of formed stool to send to a lab. The amount of elastase in the stool is then measured. Only formed stool should be used (no liquid stool). If liquid stool is submitted, this test may not be accurate, because dilution can cause the result to appear falsely abnormal.
Too much fat in the stool is a sign that food is not being broken down and absorbed properly. There are two kinds of fecal fat tests.
Qualitative test: For this test, one sample of stool is collected and sent to a lab. This sample is studied under a microscope and the amount of fat is assessed.
Quantitative fecal fat: For this test, you are asked to eat a specific amount of fat over several days. Then, stool samples are collected for two to four days. These samples are then studied and measured in a lab for fat.
When food enters the duodenum from the stomach, a hormone called secretin is released. This hormone triggers the pancreas to send digestive enzymes into the duodenum. The secretin stimulation test checks whether the pancreas has a normal response to secretin.
During the test, secretin is given by intravenous (IV) line. Then, fluid from the duodenum is collected and tested. The fluid is most commonly collected during a procedure called endoscopy. If you have this test, your health care provider can tell you more about how it will be done.
Treatments for exocrine pancreatic insufficiency
Pancreatic enzyme replacement therapy
To get the most out of PERT, follow all the instructions you are given, including the following:
- Take all the capsules at the start of the meal, with the first mouthful of food. For a large or long meal, you can take half at the start and half at the end.
- Swallow the capsules with a cold (not hot) drink.
- Do not take capsules on an empty stomach.
- If you have any side effects from the enzymes (such as constipation or stomach upset), tell your health care provider. An adjustment in dosage may help. Side effects also often lessen or go away with time.
- Aim to eat a nutritious diet. A diet high in vegetables, fruits, whole grains and healthy proteins is best.
- Do not avoid eating fat. Fat is needed for absorption of many essential vitamins. For some diseases (such as cystic fibrosis), a higher-fat diet is helpful. Work with your health care provider to determine the level of fat in your diet that is best for you.
- Some patients have better results eating smaller meals more often. Pay attention to your body and make adjustments that work for you.
- Talk to your health care provider before taking any new medications, supplements or herbal remedies. In some cases, these may affect your pancreas.
Reviewed by


